Clinical Differential Diagnosis
Hepatic insufficiency (cirrhosis due to chronic active hepatitis, Labrador hepatopathy) with secondary cholestasis, cholangitis),pyelonephritis, neoplasia affecting the liver, biliary system, spleen (with metastases to the liver) or possibly the kidneys. Based upon original presentation and blood work results: Hyperadrenocorticism pituitary dependent or adrenal dependent tumor (adenoma or adenocarcinoma), or an adrenal tumor causing the overproduction of sex hormones (atypical Cushing's disease). This ddx becomes less likely when he is presented 2 weeks later for signs of anorexia, vomiting and polydipsia, at which point, neoplasia becomes much more likely, whether affecting the liver, kidneys, adrenal gland(s), intestinal tract and/or pancreas.
Image Interpretation
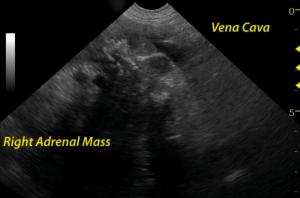
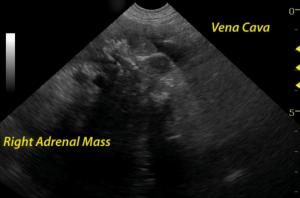
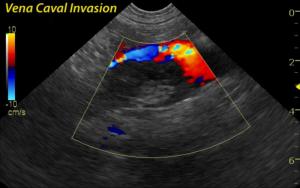
The area of the right adrenal gland and vena cava (CVC) notes an aggressive mineralizing mass deriving from the right adrenal gland and invading the CVC in the region of the phrenic vein. No adrenal architecture is noted. The vena cava is expanded by the occupied mass. Attached thrombus likely also is responsible for part in the intra caval mass accumulation.The liver image revealed multifocal mixed hyper and hypoechoic nodular changes with disruption of hepatic infrastructure and "target" type appearance strongly suggestive for metastatic disease owing to the aggressive and invasive right adrenal mass. Color flow Doppler evidences the persistence of venous flow around the mass.
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis
Invasive mineralizing right adrenal mass, non resectable - likely adenocarcinoma owing to the invasive appearance and mineralization . Pheochromocytoma less likely (few pheochromocytomas mineralize). Multiple "target" liver lesions strongly suggestive for metastatic disease.
Outcome
A recheck exam was performed one month later and he was found to have pale pink mucous membranes, a pendulous abdomen with a positive fluid wave on ballottment. Repeat blood chemistry revealed hypoproteinemia, hypoalbuminemia, elevations of the ALT, AST and GGT enzyme activities, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia and hypomagnesemia. The CBC showed the presence of decreased numbers of RBCs and a decreased hematocrit, and a leukocytosis consisting of a neutrophilia and monocytosis. The urinalysis showed a high pH, low specific gravity, and trace hematuria. The patient was then lost to follow-up.