Clinical Differential Diagnosis
Hyperadrenocorticism - pituitary dependent or adrenal dependent tumor (adenoma or adenocarcinoma), adrenal tumor causing the overproduction of sex hormones (atypical Cushing's disease). Hyperlipidemia, chronic active hepatitis, cholestasis, vacuolar hepatopathy.
Image Interpretation
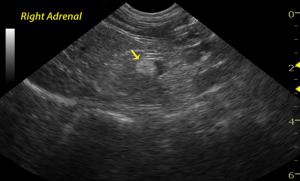
The right adrenal gland is enlarged with irregular contour, mass appearance, and focal hyperechoic nodule at the caudal pole. Loss of structural detail is evident. An intimate relationship with the vena cava is present without obvious invasion. The left adrenal is uniform with normal size and contour indicating a unilateral pathological process.
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis
Left adrenal mass, non invasive - adenoma, adenocarcinoma, pheochromocytoma, and less likely benign hyperplasia.
Sampling
Surgical biopsy showed right adrenocortical adenoma.
Outcome
The patient was referred to a board certified surgeon for an exploratory surgery. A cholecystectomy was performed due to concurrent gall bladder mucocele (diagnosed sonographically). Culture and sensitivity of the bile was negative for bacterial growth. A biopsy of the gallbladder showed marked cystic, mucinous, gallbladder hyperplasia. The liver sample revealed mild, chronic, lymphocytic hepatitis with a hydropic vacuolar hepatopathy. A 3 cm long adrenal mass was visualized, and a right adrenalectomy was performed. The dog did well post-operatively and is doing well clinically according to the owner.