Clinical Differential Diagnosis
Diabetes mellitus in conjunction with pancreatitis, hypoaldosteronism secondary to an adrenal mass, such as an adenocarcinoma or adenoma.
Outcome
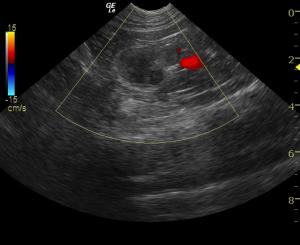
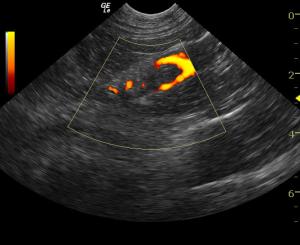
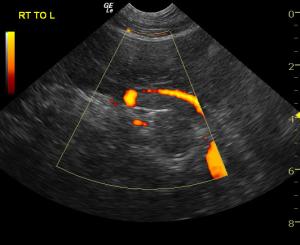
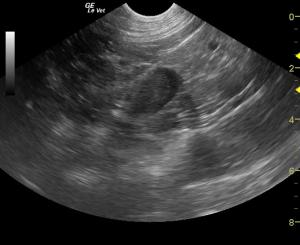
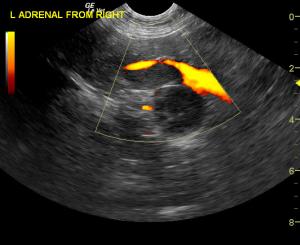
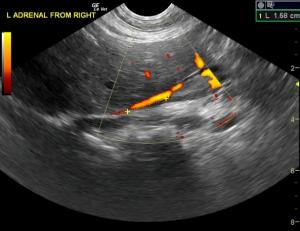
The patient was referred for an abdominal CT scan. A heterogeneous, hypodense soft tissue mass obliterated the normal architecture of the left adrenal gland. There was also invasion of the caudal vena cava at the junction of the left renal vein and the middle of the mass. The right adrenal gland was not visualized. A focal, hypodense nodule was present in the caudate liver lobe. The cat was suspected to have a neoplasm affecting the left adrenal gland with metastases to the caudal vena cava, as well as possible left renal vein involvement. Presence of metastases to the liver could not be ruled out as not all of the liver was included in the study. Medical management was determined to be the best option in this case, as the patient was not considered a good candidate for surgery.