"What Does This?" The ubiquitous question we all ask ourselves when a clinical presentation walks through our door. In the northeast rainstorms come through and here comes the Lepto caseload 3-7 days later like a shadow behind the storm. Come see what Pennsylvania Mobile sonographer Rebekah Jakum RVT/RVT (http://www.pamobile.net/) found on this geriatric Aussie successfully managed by the staff at Rossmoyne Veterinary Emergency Center in Harrisburgh, PA (http://raetc.com/).
Lepto cases can present with a rapid onset of "ADR," renal +/- liver failure and a particular sonographic renal presentation that may be structurally normal owing to acute insult. Or, the kidneys may present in this manner shown here with mild archotectural distortion and pericapsular fluid formation. Or, in chronic cases, a chronic interstitial pattern may be present. Do a basic search on sonopath on your Iphone or Android App or through the site and see what we see from the inside out (http://sonopath.com/members/case-studies/search?text=leptospirosis&species=All).
Clinical Differential Diagnosis
Acute kidney injury – toxic, infectious (Leptospira, bacterial nephritis, septicemia), hypoxia, renolith, ureteral obstruction, lymphoma.)
ALT elevation: inflammatory or reactive hepatopathy
Image Interpretation
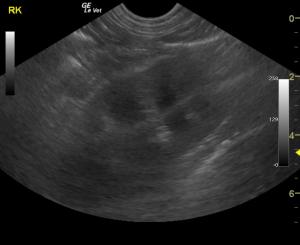
The right kidney presented cortical infarct at the caudal pole. The right kidney measured 7.06 cm.
The left kidney measured 6.97 cm. Pericapsular fluid pattern was noted around both kidneys (more evident on left caudal pole) with
disruption of the corticomedullary definition. Slight pyelectasia was noted in the left kidney as well.
Ill defined pericapsular fat was noted primarily around the left kidney indicative of inflammation. . The gallbladder presented suspended debris and double layered wall. The cystic duct was dilated as was the common bile duct at 0.36 cm. This is consistent with immature mucocele. The liver presented a mild increase in the portal markings.
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis
Acute nephritis presentation with pericapsular fluid accumulation. Immature gallbladder mucocele. Suspect Leptospirosis or acute renal toxin.
Sampling
Lepto Titer strong positive.
DX
Acute nephritis presentation with pericapsular fluid accumulation. Immature gallbladder mucocele. Suspect Leptospirosis or acute renal toxin.
Outcome
The patient tested strong positive for Leptospirosis and responded to medical therapy. See the happy patient sporting his handsome e-collar and doing well!




Comments
Treatment for renal failure is recommended. Blood pressure, GI protectants, and IV Ampicillin is warranted given the strong potential for Leptospirosis. Plasma transfusion with plasma expanders would be ideal. Urine culture and sensitivity is warranted. Assessment for toxin exposure would also be recommended such as Aflatoxin or plant ingestion. Core renal biopsy may be necessary. Dialysis would be ideal if refractive to therapy.
Note: The pericapsular renal fluid accumulation is a frequent sonographic finding in cases of Leptospirosis that we see in the northeast United States, the elevated renal _/- liver enzymes wiht depression and relkatively minor sturctural renal changes wiht pericapsular fluid accumulation is a personal red flag for leptospirosis. Of course other acute renal insults can do this but since the northeast uinited states is endemic for leptsopirosis we must consider it on the forefront, especially in the days following heavy rain in the region.