Clinical Differential Diagnosis
(Cariota DACVIM):
Hemangiosarcoma
Hemangioma
Splenic abscess
Splenic torsion
Other neoplasia
Image Interpretation
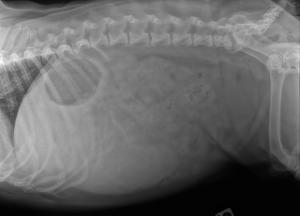
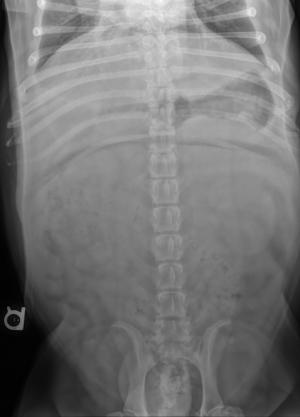
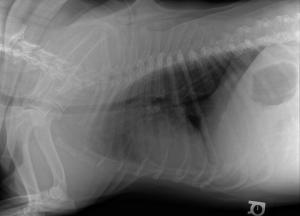
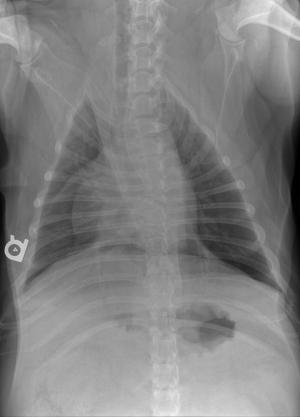
Radiographic Interpretation (Yanik DACVR, Illumipet.com): Abdominal study: Images 1 & 2: Marked splenomegaly strongly suspected to be secondary to torsion. Accompanying infiltrative or neoplastic pathology cannot be ruled out. Small volume of peritoneal effusion and/or inflammation likely secondary to the splenic pathology. Thoracic study: Images 3 & 4: Mild microcardia and underperfused pulmonary vasculature support of hypovolemia. Atypical intrathoracic fat distribution, which is consider incidental. Multiple hemivertebrae.
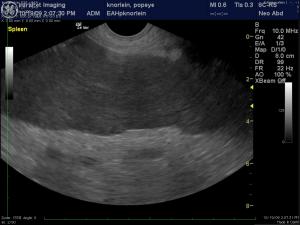
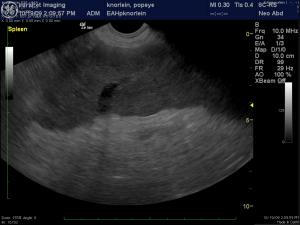
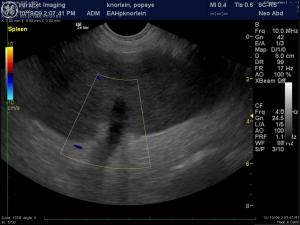
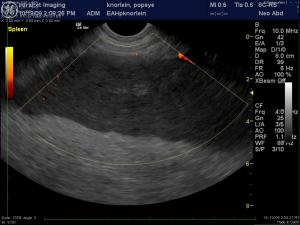
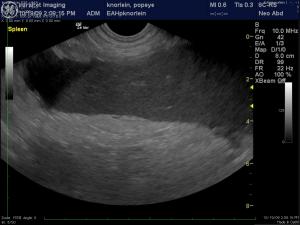
(Yanik DACVR/Lindquist DABVP): Images 5 & 6 demonstrate a canine spleen with mildly heteroechoic, moderately hypoechoic parenchyma, echogenic vascular walls, scalloping capsular contour and increased pericapsular fat echogenicity. Image 7 demonstrates complete lack of blood flow in the hilar vessels given the lack of color flow uptake over the anechoic vessel. Image 8 demonstrates minimal power Doppler uptake over the coarse and micronodular splenic parenchyma. Image 9: The free fluid associated with this presentation indicates either hemorrhage or transudate deriving from an infiltrative process. The video (Image 10) demonstrates a dilated splenic vessel with echogenic content in the far field likely indicating thrombosis given the complete lack of power flow uptake neither within the vessel nor the parenchyma.
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis
(Yanik DACVR/Lindquist DABVP): Hypo-avascular parenchymal splenic pathology owing to splenic thrombosis, infarction with likely underlying splenic torsion and/or infiltrative process such as lymphoma or other round cell neoplasia. Immediate splenectomy is recommended or US-guided sampling if multiple organs appear affected.
Sampling
(Ward DVM Eastern A.H., Baltimore, MD): Surgical Dx: Splenic Torsion.
Splenectomy revealed marked acute and chronic hemorrhage with mild hemosiderosis. Thrombosis and marked acute hemorrhage of adjacent vessels. Collagenous fibrosis and cartilaginous metaplasia and dystrophic mineralization present in one vessel. No evidence of neoplasia.
Outcome
(Parkinson RDMS, Ward DVM, Lindquist DABVP): Abdominocentesis revealed blood in the abdomen prior to surgery. The patient responded well to splenectomy and recovered uneventfully post-op.


Comments