Clinical Differential Diagnosis
(Remo Lobetti PhD, DECVIM):
GI tract - IBD/neoplasia/foreign body
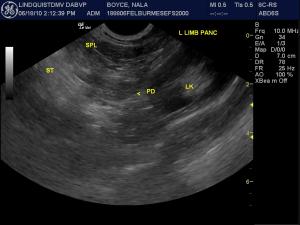
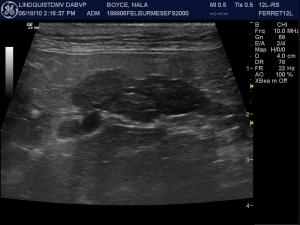
Pancreas - pancreatitis/neoplasia/cyst/abscess
Liver - cholangio-hepatitis/hepatitis/neoplasia
Peritonitis
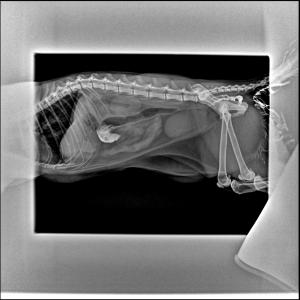
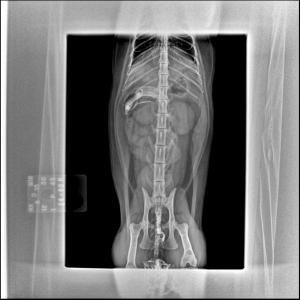
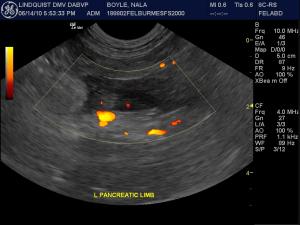
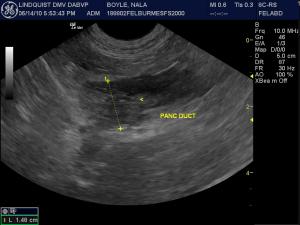
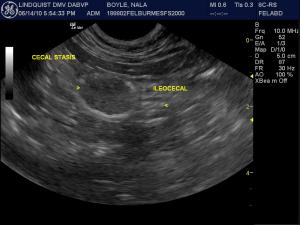
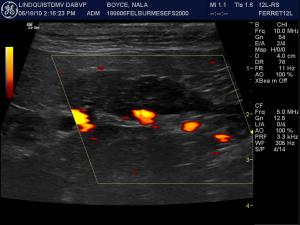
Sonographic Differential Diagnosis
(Lindquist DMV, DABVP): Pancreatic necrosis/pancreatitis with possibility of pancreatic carcinoma, lymphoma, or nodular hyperplasia.
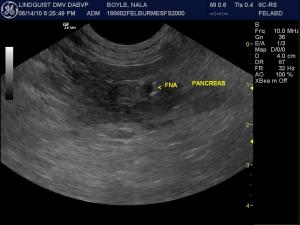
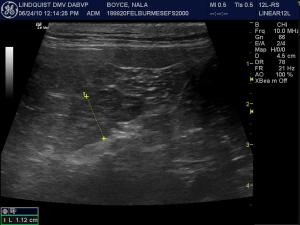
Sampling
(Lindquist DMV, DABVP): US-guided fine needle aspiration of multiple areas of the pancreas revealed well differentiated pancreatic cells with increased neutrophils admix with blood consistent with suppurative inflammation. US-guided fine needle aspiration of the spleen also revealed suppurative inflammation.
Outcome
The patient was stable as an outpatient after 1 month of zithromax and hypoallergenic diet.


Comments