Sampling
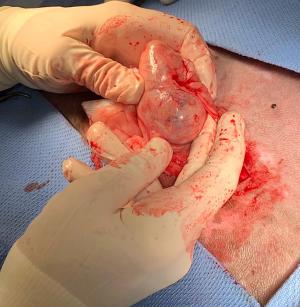
Tru-cut surgical biopsies of the mass were taken during exploratory surgery.
DX
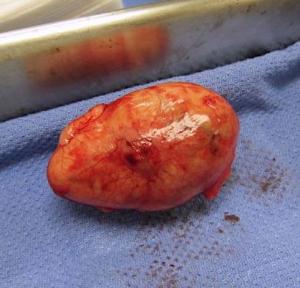
Necrotic adipose tissue with granulomatous inflammation and fibrous encapsulation
Outcome
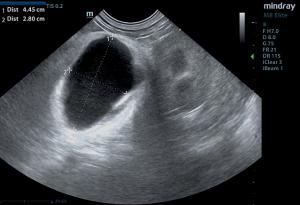
The caudal abdomen revealed a 4.45 x 2.8 cm hypoechoic abscess or infarcted lipoma with hyperechoic
granulation bed and inflammation with slight fluid accumulation noted around the abscess. Surgical intervention was recommended. The patient underwent an exploratory surgery and the mass was remove. The mass was determined to be necrotic adipose tissue with granulomatous inflammation and fibrous encapsulation, most compatible with an intra-abdominal lipoma or strangulated omental fat, which has become necrotic and secondarily inflamed. The patient was found to be doing great and fully recovered at suture removal appointment.