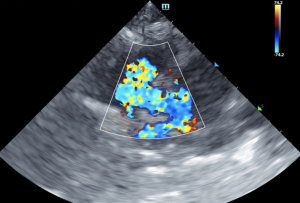
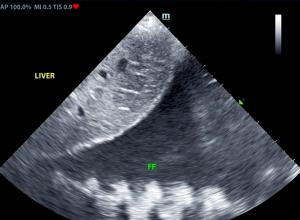
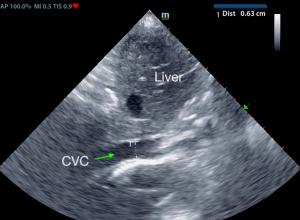
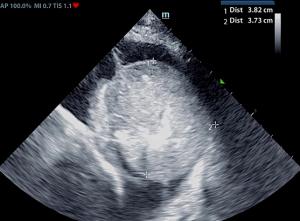
Echocardiograms are vital for the diagnosis and management of cardiac disease. Changes in the heart can develop slowly, or in the case of this patient, who has a ventricular septal defect (VSD), can progress more rapidly. The patient was diagnosed with VSD at his initial ultrasound. Within 4 months, the patient had gone into congestive heart failure with a moderate amount of pleural effusion present. 8 months from the initial ultrasound, the patient was dealing with a large amount of pleural effusion and a large thoracic mass was discovered. Serial ultrasounds performed by Kelly Vazquez, CVT, SDEP® certified clinical sonographer for SonoPath Mobile Veterinary Ultrasound; specialist interpretations by Eric Lindquist, DMV, DABVP, Cert. IVUSS, Maggie Machen, DVM, DACVIM (Cardiology) and R. McKenzie Daniel, DVM, DABVP.
DX
Ventricular septal defect • Eisenmenger's physiology • Right sided volume overload • Pleural effusion • Hepatic congestion • Thoracic mass
Outcome
Initial echo: Concern for right sided heart failure. Prognosis long term is poor. This is a congenital lesion with secondary emerging right sided heart failure.
At 4-month recheck: The cause of bi-cavitary effusion is right-sided cardiomyopathy. There are severe right heart compensatory changes, which would suggest elevated risk for decompensation. Immediate hospitalization and lifelong cardiac support is recommended. Thoracocentesis and/or abdominocentesis should be considered to improve patient stability.
At follow up echo 8 months later: Complex case with significant right cardiomyopathy. Given the age of the patient and this presentation, potential considerations may include stenotic disease, tricuspid dysplasia, non-obvious pulmonary hypertension, or other congenital vs. acquired defect. The pleural effusion may be multi-factorial in origin given the concurrent unspecified pericardial to thoracic mass lesion, although given evidence of early hepatic congestive criteria, the patient is likely technically in right heart failure. A very guarded to potentially unfavorable prognosis is likely indicated.
At the time of this article, the owners were keeping the patient as comfortable as possible with thoracocentesis to aspirate the pleural effusion, making breathing easier and buying this sweet, velvety fellow a bit more time.





Comments
Ventricular septal defects (VSDs) are most commonly located in the perimembranous portion of the septum, high in the ventricular septum immediately beneath the right and noncoronary aortic valve cusps on the left and just below the cranioseptal tricuspid valve commissure on the right. They vary in size and hemodynamic significance. Doubly committed juxta-arterial septal defects (located beneath the aortic valve on the left and beneath the pulmonic valve on the right) and muscular septal defects (located at any site along the muscular septum) may also be seen. Ventricular septal defects may be seen with other congenital cardiac anomalies. Credit: MSD Manual LINK
Congestive heart failure (CHF): Left-sided congestive heart failure occurs when the pressure inside the blood vessels in the lungs increases causing fluid to seep from the vessels into the surrounding lung tissue. Right-sided congestive heart failure is similar to left, but causes pleural effusion and/or abdominal ascites. Credit: MSD Manual: LINK.
Eisenmenger’s physiology describes changes that occur when a left to right shunting cardiac defect, eg VSD, PDA, causes pulmonary overperfusion, leading to pulmonary hypertension and eventually reversed shunting (right to left) as the right heart pressures increase and become equal to or greater than systemic arterial pressures. Credit: Vetlexicon™ LINK.